Gibbs Free Energy Formula In Electrochemistry
Gibbs Free energy formula is given below. The formula of the Gibbs Free Energy links thermodynamics and electrochemistry.
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn And9gct7sgsfd7sdex5ds3wvtw9zfebcddxg2cbbn4cemnikv3umnpi8 Usqp Cau
G is the change of Gibbs free energy for a system and G is the Gibbs energy change for a system under standard conditions 1 atm 298K.
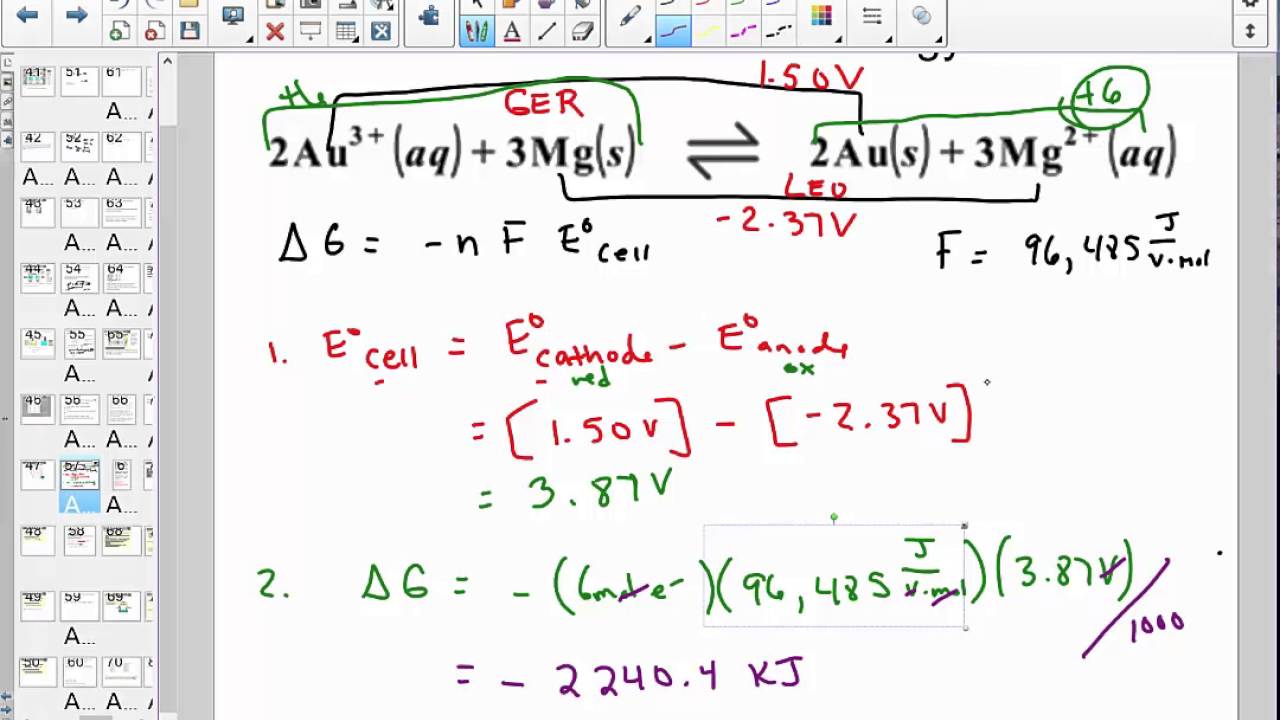
Gibbs free energy formula in electrochemistry. ΔG nFE cell 6 mole96 485 J V mol027 V 156 104 J 156 kJ mol Cr2O2 7. 3 B r X 2 l 2 N a s 2 N a X a q 2 B r X a q In this case we have n 2 as there are two electrons being transferred in this reaction from bromine to sodium. Of electrons involved in the reaction.
The relation between the Gibbs free energy and the electrical potential is. Δ r G -nFE cell Δ r G Standard Gibbs energy of the reaction. If each electron carries a charge of 1 f aradayF and n number of moles of electrons are transferred then the total charge transferred is n F.
EqDelta Gcirc -nFE_cellcirc eq where. Faradays constant F is defined as the charge on one mole of electron. Where g is the difference in the energy between reactants and products.
Where G is the difference in the energy between reactants and products. See full answer below. This video is discuss about Gibbs free energy and its application relation between Gibbs energy and equilibrium constant it discuss about conductance of.
E cell Standard potential of the cell. Use the data in Table P2 to calculate ΔGo for the reduction of ferric ion by iodide. Calculate the standard Gibbs energy of the cell reaction Given.
Z is the valence of the electrochemical reaction and F is the Faraday constant. Based on Gibbs work Nernst extended the theory to include the contribution from. Formula for gibbs free energy in electrochemistry.
Δ G z F E. The maximum work done is the amount of energy produced given by the decrease in the thermodynamic property called Gibbs free energy. I dont see how the moles of this reaction is 2 when there are 3 moles of I -.
Where g is the difference in the energy between reactants and products. Give relation between standard Gibbs energy of the reaction Δ r G and standard potential of the cell. To construct a full reaction for this cell the usual procedure taught is to take 1 multiply it by 2 and subtract it from 2.
In the late 19th century Josiah Willard Gibbs formulated a theory to predict whether a chemical reaction would be spontaneous based on free energy. Has Eocell 0236 V at 298 K. The Change in Gibbs free energy if cell potential is given formula is defined as the negative product of cell potential to the total charge transferred during the reaction nF and is represented as G -nFaradayEcell or gibbs_free_energy -Moles of electron transferredFaradayCell potential.
F e N A. On an energy diagram G can be represented as. ΔG ΔGo RTln Q Δ G Δ G o RT ln Q.
The free part of the older name reflects the steam engine origins. 1F 96500 Cmol CBSE 2017 The standard Gibbs free energy G can be obtained from the equation. The Gibbs free energy of a system at any moment in time is defined as the enthalpy of the system minus the product of the temperature times the entropy of the system.
Thus ΔGo is 156 kJ for the reaction as written and the reaction is spontaneous. If at equilibrium the Δ G is zero this means that also E is zero but this is not true because E at equilibrium is the equilibrium potential of the electrochemical reaction considered. ΔH change in enthalpy.
G H - TS The Gibbs free energy of the system is a state function because it is defined in terms of. For example in 139 we are asked to calculate the Gibbs Free Energy for 2Ce 4aq 3I -aq -----2Ce 3aq I 3-aq with an E cell of 108v.
Free Energy
Free energy in thermodynamics energy-like property or state function of a system in thermodynamic equilibrium. Free Energy Device Pseudoscience - A hypothetical perpetual motion device that creates energy thereby contradicting the laws of thermodynamics.

Most Powerful Free Energy Generator Using Neodymium Activity Youtube
Build solar farms that collect the Sun power.

Free energy. A thermodynamic quantity that is the difference between the internal energy of a system and the product of its absolute temperature and entropy. Specific free energy is an intensive variable. The output power is much higher than the input power.
Harvest the wind energy using wind turbines. We can obtain energy from sources that do not require an input that we have to pay for such as other forms of energy including fuel oil and coal. Free energy is used to determine how systems change and how much.
Free energy A process will only happen spontaneously without added energy if it increases the entropy of the universe as a whole or in the limit of a reversible process leaves it unchanged this is the Second Law of Thermodynamics. To begin with free energy refers to the idea of a system that can generate power by taking energy from a limitless source. But to me at least thats kind of an abstract idea.
FREE ENERGY FOR YOUR HOME GARAGE CAR OR TRUCK. Electrons flowing through the load flow in from the environment attracted by this bait pumped in NOT A SINGLE ELECTRON USED FOR EXCITING AMBIENT. The Gibbs free energy measured in joules in SI is the maximum amount of non-expansion work that can be extracted from a thermodynamically closed system one that can exchange heat and work with its surroundings but not matter.
The free energy F U TS is an extensive variable. This device takes a low-power 110 Volt AC input and produces a much higher-power electrical output which can be used for powering much greater loads than the input could power. Use nuclear fission to generate electricity.
A true free energy motor and generator all in one unit. Video shows our motor generator running itself and stopping a house meter Dead in its tracks. This is free-energy under whatever name you like to apply to it.
The free energy perturbation theory has been applied to a number of problems in the areas of proteinligand interactions site-directed mutagenesis in proteins nucleic. This Free-Energy device generates an AC electrical potential in ambient space bait for electrons 2. The specific free energy f in the wider literature the letter a is also used is defined as 38 f u Ts.
How to make money from nothing free energy All you have to do in order to make money from nothing is. The Helmholtz free energy or simply free energy is another thermodynamic potential. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device.
To build huge hydroelectric dams that produce electricity from the energy of falling water and running water. - The World of Free Energy - Current State - This Incredible System Generates Electricity from Living Plants - This Invention Must Be Big - Why Else Would So Many Want to Stop It - Free Energy - This Material can Harvest Energy from the Sun Heat and Movement. Free energy is what we can find from our local environment and use without having to suffer costs.
Free energy is a thermodynamic quantity equivalent to the capacity of a system to do work. This maximum can be attained only in a completely reversible process. The capacity of a system to do work as in an exothermic chemical reaction.
Free energy has the dimensions of energy and its value is determined by the state of the system and not by its history.
Free Radicals Definition
American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language Fifth Edition. These molecules called free radicals have a free electron which makes the molecule highly unstable.

Thirteen Ways To Keep Free Radicals Away And Why It S So Important
In biological systems free radicals are deactivated by anti-oxidants uric acid and certain enzyme activities.

Free radicals definition. Oxygen free radicals can be very damaging to DNA and proteins and to the fat in cell membranes where a free radical chain reaction can be set up. One that is produced in the body by natural biological processes or introduced from an outside source such as tobacco smoke toxins or pollutants and that can damage cells proteins and DNA by altering their chemical structure. Free radicals are unstable atoms that can damage cells causing illness and aging.
An atom or atom group carrying an unpaired electron and no charge. Theyre linked to multiple illnesses including diabetes. A radical in its usually transient uncombined state.
The damage from these chemicals can lead to cancer and other health conditions. Eg hydroxyl and methyl Free radicals may be involved as short-lived highly active intermediates in various reactions in living tissue notably in photosynthesis. This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other.
Free radical definition an atom or molecule that bears an unpaired electron and is extremely reactive capable of engaging in rapid chain reactions that destabilize other molecules and generate many more free radicals. Free radicals Highly chemically active atoms or group of atoms capable of free existence under special conditions for very short periods each having at least one unpaired electron in the outer shell. Free radicals are linked to aging and a host of diseases.
An atom or group of atoms that has at least one unpaired electron and is therefore unstable and highly reactive. Definition and Structure of Free Radicals. Free radicals are uncharged very reactive and short-lived molecules.
The free radicals collide with your cells in an attempt to steal an electron and the cells that lose electrons may start to malfunction. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. Free radical definition is - an especially reactive atom or group of atoms that has one or more unpaired electrons.
They form when atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons resulting in an unpaired electron. Free radicals are a byproduct of normal cell function. In the body deactivated by antioxidants uric acid and certain enzyme activities.
When cells create energy they also produce unstable oxygen molecules. Human beings contain 1000020000 free radicals which attack each and individual cell of our body. In animal tissues free radicals can damage cells and are believed to accelerate the progression of cancer cardiovascular disease and age-related diseases.
Free radicals are compounds that can cause harm if their levels become too high in your body. Free radicals can damage your cells and your DNA through a process called oxidation. Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselvesa process that can cause damage to DNA and other parts of human cells.
Free radicals are unstable molecules or atoms that can damage the cells in your body. Free radicals are capable of starting rapid chain-reactions that destabilize the ions in other nearby molecules generating more free radicals. The most common definition of free radicals is molecules or molecular fragments containing one or more unpaired electrons in atomic or molecular orbitals 3.
