Gibbs Free Energy Formula In Electrochemistry
Gibbs Free energy formula is given below. The formula of the Gibbs Free Energy links thermodynamics and electrochemistry.
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn And9gct7sgsfd7sdex5ds3wvtw9zfebcddxg2cbbn4cemnikv3umnpi8 Usqp Cau
G is the change of Gibbs free energy for a system and G is the Gibbs energy change for a system under standard conditions 1 atm 298K.
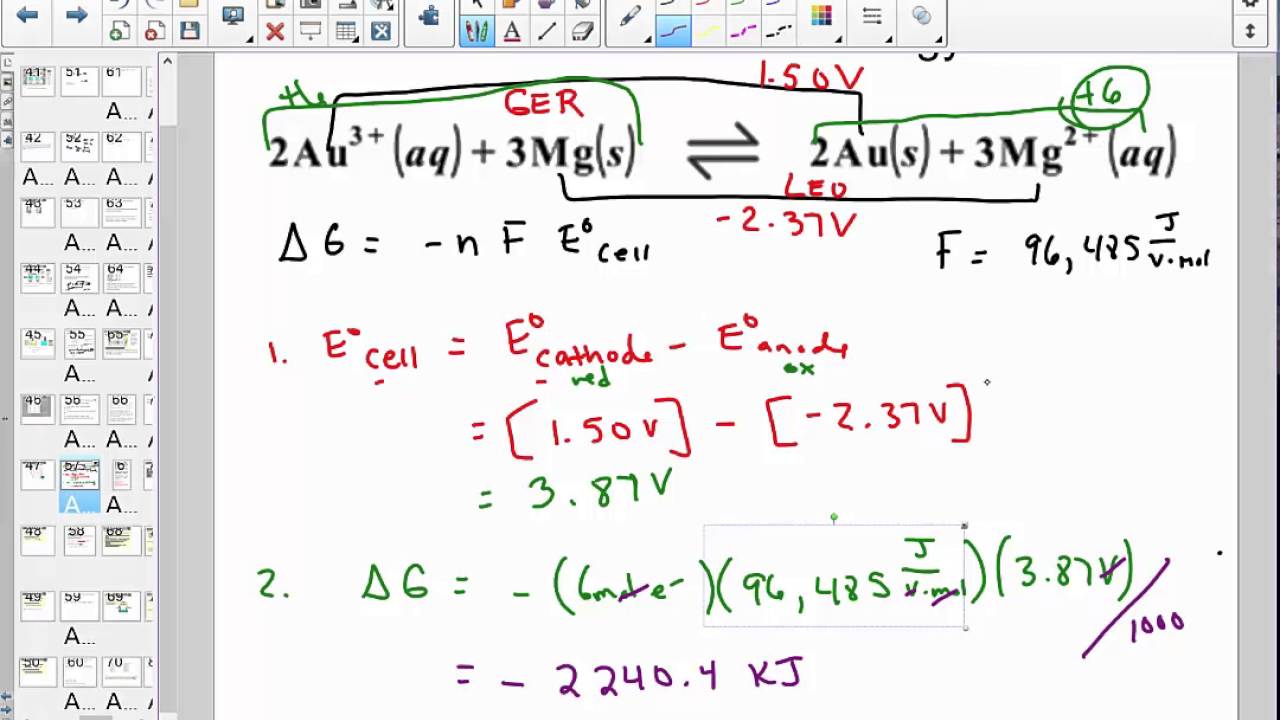
Gibbs free energy formula in electrochemistry. ΔG nFE cell 6 mole96 485 J V mol027 V 156 104 J 156 kJ mol Cr2O2 7. 3 B r X 2 l 2 N a s 2 N a X a q 2 B r X a q In this case we have n 2 as there are two electrons being transferred in this reaction from bromine to sodium. Of electrons involved in the reaction.
The relation between the Gibbs free energy and the electrical potential is. Δ r G -nFE cell Δ r G Standard Gibbs energy of the reaction. If each electron carries a charge of 1 f aradayF and n number of moles of electrons are transferred then the total charge transferred is n F.
EqDelta Gcirc -nFE_cellcirc eq where. Faradays constant F is defined as the charge on one mole of electron. Where g is the difference in the energy between reactants and products.
Where G is the difference in the energy between reactants and products. See full answer below. This video is discuss about Gibbs free energy and its application relation between Gibbs energy and equilibrium constant it discuss about conductance of.
E cell Standard potential of the cell. Use the data in Table P2 to calculate ΔGo for the reduction of ferric ion by iodide. Calculate the standard Gibbs energy of the cell reaction Given.
Z is the valence of the electrochemical reaction and F is the Faraday constant. Based on Gibbs work Nernst extended the theory to include the contribution from. Formula for gibbs free energy in electrochemistry.
Δ G z F E. The maximum work done is the amount of energy produced given by the decrease in the thermodynamic property called Gibbs free energy. I dont see how the moles of this reaction is 2 when there are 3 moles of I -.
Where g is the difference in the energy between reactants and products. Give relation between standard Gibbs energy of the reaction Δ r G and standard potential of the cell. To construct a full reaction for this cell the usual procedure taught is to take 1 multiply it by 2 and subtract it from 2.
In the late 19th century Josiah Willard Gibbs formulated a theory to predict whether a chemical reaction would be spontaneous based on free energy. Has Eocell 0236 V at 298 K. The Change in Gibbs free energy if cell potential is given formula is defined as the negative product of cell potential to the total charge transferred during the reaction nF and is represented as G -nFaradayEcell or gibbs_free_energy -Moles of electron transferredFaradayCell potential.
F e N A. On an energy diagram G can be represented as. ΔG ΔGo RTln Q Δ G Δ G o RT ln Q.
The free part of the older name reflects the steam engine origins. 1F 96500 Cmol CBSE 2017 The standard Gibbs free energy G can be obtained from the equation. The Gibbs free energy of a system at any moment in time is defined as the enthalpy of the system minus the product of the temperature times the entropy of the system.
Thus ΔGo is 156 kJ for the reaction as written and the reaction is spontaneous. If at equilibrium the Δ G is zero this means that also E is zero but this is not true because E at equilibrium is the equilibrium potential of the electrochemical reaction considered. ΔH change in enthalpy.
G H - TS The Gibbs free energy of the system is a state function because it is defined in terms of. For example in 139 we are asked to calculate the Gibbs Free Energy for 2Ce 4aq 3I -aq -----2Ce 3aq I 3-aq with an E cell of 108v.
